There are many similarities between the terms physiotherapy and physical therapy and the focus of each within the allied health professions. The topics range from being equal in performance to varying degrees of distinction. So, are they the same, similar, or vastly different?
According to Wikipedia, the terms are interchangeable, stating, “Physical therapy, also known as physiotherapy…”. However, definitions among other resources give separate definitions based on the approach used by physiotherapists and physical therapists and their location.
If living in Europe, Canada, or Australia, one may hear physiotherapy used, while those living in America are familiar with physical therapy.
One commonality is that neither Physiotherapists nor Physical Therapy Clinics prescribe drugs, and medical, and chiropractic physicians refer most patients.
What exactly is the general function of each?

The main difference between physical therapy and physiotherapy is how they focus on healing. Physiotherapists typically use a manual, hands-on approach with soft tissue and fascial releases, stretches, and massages. On the other hand, physical therapy uses hands-on therapy but adds an exercise-based approach. Both educate patients through recovery on ways to manage the injury, illness, or disability.
The best way to determine any difference is to define the approach of each.
What is Physical Therapy?
The American Physical Therapy Association (APTA) defines a physical therapist as “a trained and licensed medical professional with experience diagnosing physical abnormalities, restoring physical function and mobility, maintaining physical function, and promoting physical activity and proper function.”
Therefore, physical therapy treatment aims to ease chronic and acute pain, help a person function, move, and live a restored life while focusing on a specific area for treatment.
Patients seeking care from physical therapists have experienced pain from various injuries or immobility. These may include recoveries from surgeries, accidents, sports injuries, or birth/growth defects.
Physical therapists generally treat non-threatening injuries by assessing and caring for musculoskeletal issues. The problems associated with the muscles can result from strains, injuries, chronic movement issues, or recovery from surgery.
A physical therapist may work in private practice, hospitals, nursing homes, rehabilitation facilities, or fitness centers. Each location will have specialized equipment that a physical therapist will use to exercise modalities for the patient.
What is Physiotherapy?

The Chartered Society of Physiotherapy defines it as a range of interventions, services, and advice to maintain, restore, and improve people’s function and movement and maximize the quality of their lives.
The online service WebMD describes physiotherapy as “working with patients to develop customized programs designed to restore their functional ability and movement as much as possible.” Their education teaches them to help patients at all stages of life where function and activity are impacted by:
- Disease
- Health conditions
- Injury
- Environmental factors
- Aging
- Disorders
- Weight issues
From this description, one may consider that physiotherapy is a treatment that looks at a person from a “whole body” approach. Physiotherapists look at a patient from a general lifestyle and health perspective to allow them to be independent and active throughout their lives.
As with physical therapists, a physiotherapist may work in public and private hospitals, outpatient clinics, rehabilitation centers, nursing homes, and fitness centers.
Physiotherapy vs. Physical Therapy: Educational Requirements
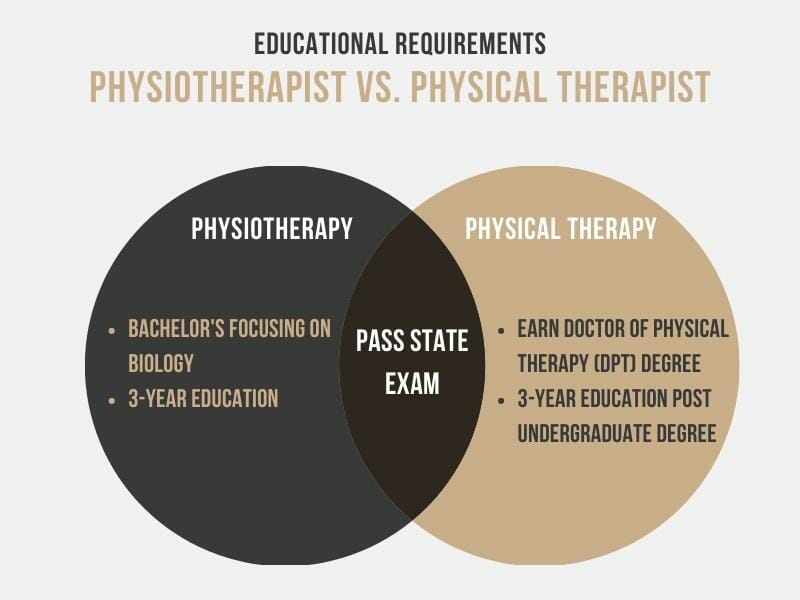
Physical Therapy: According to the American Physical Therapy Association (APTA), to practice as a physical therapist in the US, you must:
· Earn a doctor of physical therapy (DPT) degree from a Commission on Accreditation in Physical Therapy Education-accredited physical therapist education program, and
· pass a state licensure exam.
The program takes about three years and, in most cases, requires a bachelor’s degree for acceptance.
Physiotherapy: To become a physiotherapist in England, Canada, or Australia, one must have completed a bachelor’s degree focusing on biological science before applying. According to the United Kingdom’s National Health Service, the doctoral program is three years.
A full-time doctoral degree in physiotherapy (DPT) can take three years in the US, and a part-time course will take six years. A two-year accelerated Master’s course is also an option if you already have a relevant advanced degree. The requirements for licensing are the same as for a physical therapist.
Types of Therapies

The types of therapies utilized by both physical therapists and physiotherapists have much in common yet provide subtle differences.
Physical Therapy
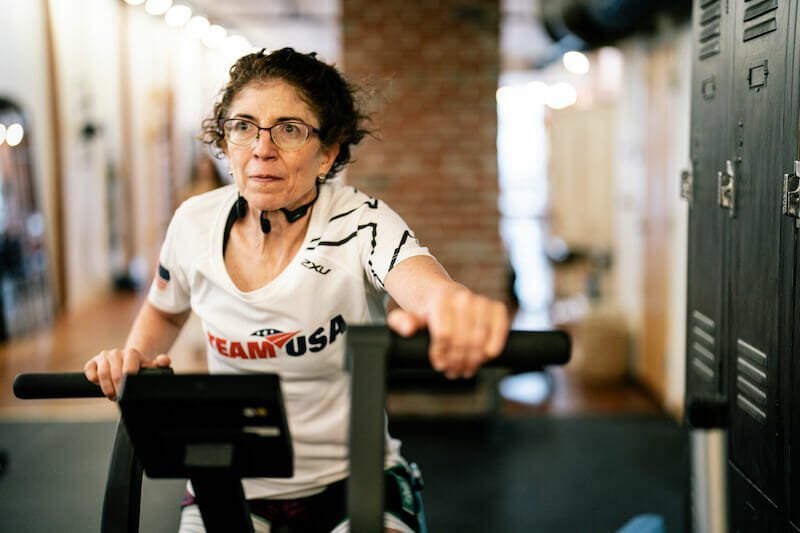

Physical Exercise
Patients receiving care from physical therapists learn contraction and relaxation exercises to increase mobility. The goal is for the patient to return to pre-injury movement and motion. Most patients can practice the exercises at home between visits and following release from care.
Hot and Cold Therapies
Patient care may include a variety of treatment modalities. These may consist of ice or cold packs, cryogenics, or nitrogen to lessen chronic and acute conditions.
Other treatments may include hot packs, diathermy, and infrared heat to treat chronic conditions and joint pain.
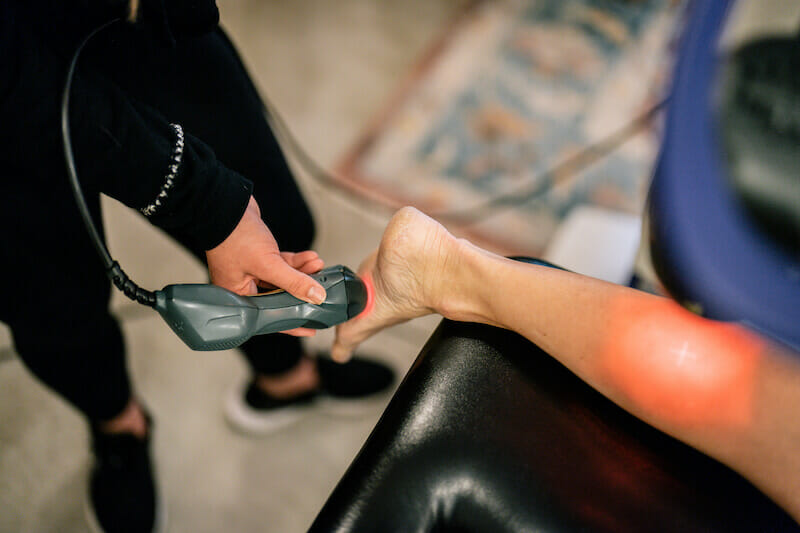

Class IV Laser Therapy
Class IV laser therapy uses specific wavelengths of light to stimulate the body’s natural healing ability. Laser therapy catalyzes your body’s healing mechanisms by improving circulation, increasing blood flow, decreasing inflammation, and encouraging the repair of cells in muscles, tendons, and joints.
Ultrasound Treatment
A DPT may use ultrasound to reduce inflammation. This treatment produces sound waves that cause vibration within the muscle, creating increased blood flow, oxygen, and chemicals necessary to heal damaged tissue.
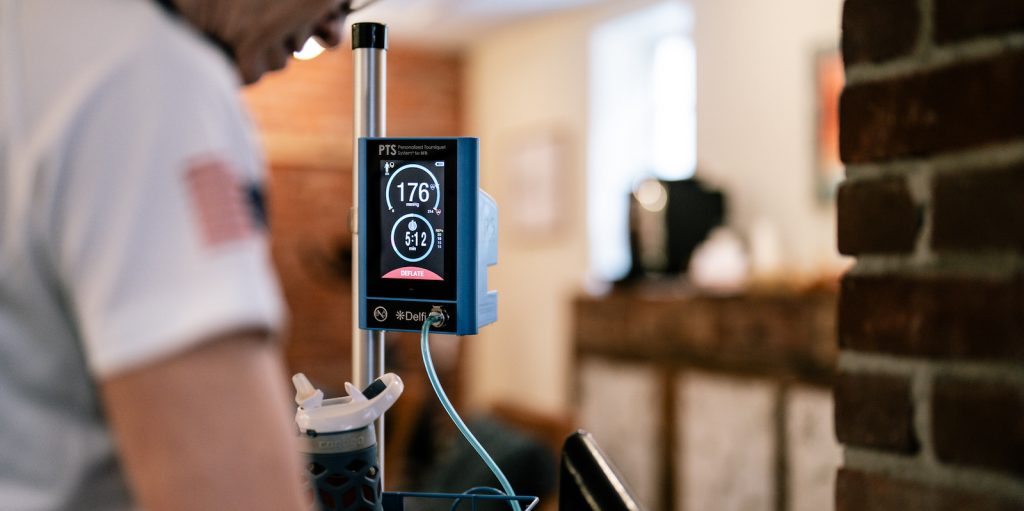

Blood Flow Restriction Therapies
Some physical therapy clinics offer Blow Flow Restriction Therapy (BFR) which allows patients limited by pain or inflammation to strengthen muscles under a smaller muscle load.
TENS Electrical Stimulation Technique
As referenced on Healthline.com, electrodes placed on the skin at the source of the pain send signals to the nerves that block or reduce pain signals to the brain.
Neuromuscular Reeducation
This technique works to restore standard body movement patterns by working the muscles in cases of atrophy, injury, or pathology.
Physiotherapy Techniques
Physiotherapy uses manual therapy often in treatment by using their hands to manipulate, mobilize, and massage the body tissues. This method forces improved blood circulation and muscle movement while relaxing the area to relieve pain and stiffness.
Physiotherapists, as noted earlier, take a holistic approach and use these manual techniques:
Massage stimulates the soft tissues to relieve pain, improve circulation, and relax.
Soft Tissue Techniques include stretching, which is a myofascial release similar to massage.
Joint Mobilization and Joint Manipulation are therapies to move a joint in a gliding manner to improve motion and joint function to control pain.
Physiotherapy Instrument Mobilization (PIM) is a technique applied with the assistance of handcrafted instruments.
Minimal Energy Techniques (METs) is a therapy that uses a muscle’s energy to relax through autogenic or reciprocal inhibition while lengthening the muscle.
Physiotherapy may include treatments such as osteopathy, acupuncture, or kinesiology
where allowed by state practice laws.
Exercises
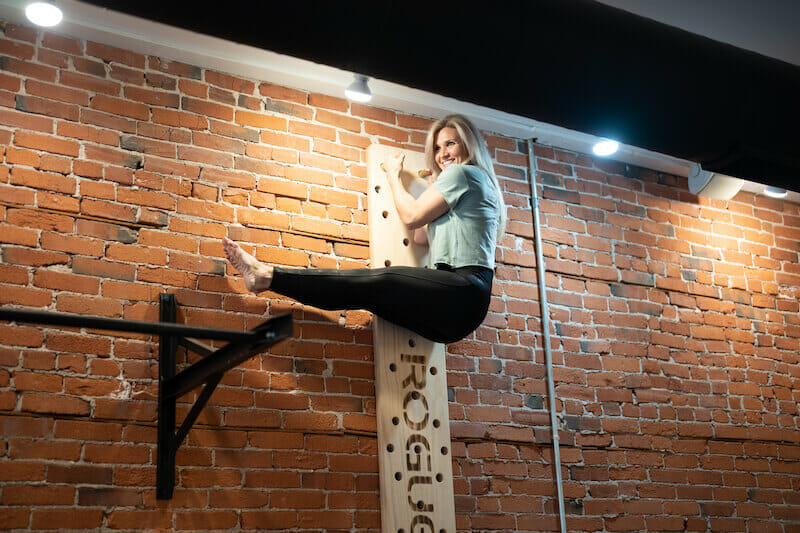

We all know the importance of exercise to one’s overall health. The movement of the body helps maintain mobility and function. In addition, many activities are easy to perform after learning proper techniques from a physical therapist.
Movement and Strength Exercises are beneficial for specific body parts to maintain posture, balance, and control, especially as we age.
Whole-Body Exercises such as swimming or walking help maintain good muscle motion and movement.
Hydrotherapy is any water exercise to support muscles and joints and build strength.
Conclusion
There are subtle differences between a physical therapist and a physiotherapist for the most part. Across the US, you will likely find the term physical therapy used, with an occasional reference to physiotherapy. A few references regarding physiotherapists are in academia and research at various universities.
Given that the requirements to practice the discipline in the US require the same education and annual post-graduate continuing education hours, you can be comfortable seeking treatment from a physical therapy practitioner.