Laser therapy is a treatment that involves the use of light-emitting diodes on the body’s surface to stimulate the body’s natural ability to heal. There are many different types and uses of Laser Therapy, including applications for dermatological treatments, surgical applications, and musculoskeletal healing/repair. Low-level laser therapy (LLLT) was cleared by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for use in the treatment of bony and soft tissue disorders in 2009 and has been successful in facilitating faster healing of musculoskeletal injuries and conditions such as arthritis and/or fractures since then.
You should know, there are different classes of lasers. These classes are categorized by the amount of power generated by the light source. Earlier research was patchy for some of the less powerful classes of LLLT (3 and 3b); however, the Class 4, higher power lasers have been quite beneficial across the board for things like muscle and bone healing.
What is Low-Level Laser Therapy (LLLT)?
Low Level Laser Therapy, commonly referred to as LLLT, is a non-invasive treatment that uses specific wavelengths of light to stimulate the body’s natural healing processes at the cellular level—without generating heat or causing damage to surrounding tissues. Unlike high-powered surgical lasers that are used to cut or destroy tissue, LLLT uses what’s called “cold” or “soft” laser light, making it ideal for therapeutic applications such as muscle recovery, soft tissue repair, and yes—bone healing.
The therapy works by applying this low-intensity light to damaged or inflamed areas, which helps to excite the mitochondria of the cells (the energy powerhouse of the body). When stimulated, these mitochondria begin producing more ATP—adenosine triphosphate—which essentially fuels the cell’s ability to repair itself and regenerate tissue. In simpler terms? LLLT helps your body do what it already wants to do—just more efficiently and with less discomfort.
LLLT is typically used in short sessions depending on the area being treated, and patients often describe the treatment as painless. Some even note a mild warmth or tingling sensation—but nothing intense. The FDA first cleared this therapy for musculoskeletal use in 2009, and since then, it’s been widely adopted by rehabilitation clinics, sports therapy centers, and medical practices specializing in pain relief and injury recovery.
Whether you’re rehabbing a stress fracture, recovering from orthopedic surgery, or trying to get ahead of chronic joint inflammation—LLLT could be a game-changer in your healing timeline. Think of it as giving your body’s natural recovery system a helpful nudge in the right direction.
What Are the Different Classes of Laser Therapy?
Not all lasers are created equal. When it comes to laser therapy, especially for healing bones and soft tissues, understanding the different classes of lasers is essential. Laser devices are categorized by their power output and potential to cause tissue damage. This classification ranges from Class 1 (very low power, such as barcode scanners) all the way up to Class 4 (high-powered therapeutic lasers).
Here’s a quick breakdown to give you a better idea:
- Class 1–2 Lasers: These are the lowest-powered lasers and are generally considered safe for everyday use. You’ll see these in things like CD players and laser pointers—technology that’s not meant for therapeutic applications.
- Class 3 & 3B Lasers: These are the types of low-level lasers that were often used in earlier versions of LLLT. While they do penetrate tissue and can promote healing, their lower power output sometimes limited the depth and effectiveness of treatment—especially for deeper tissues like bone.
- Class 4 Lasers: This is where things get exciting. Class 4 lasers are considered “high-powered” and allow for much deeper penetration into the body, delivering more energy in less time. These lasers are powerful enough to influence not only soft tissue but also dense structures like bone, tendons, and ligaments—making them ideal for musculoskeletal and post-surgical recovery. Also important: Class 4 lasers can still be used safely when administered by trained professionals.
Early studies were mixed on lower-class LLLT effectiveness for things like fractures, but the evidence supporting Class 4 laser therapy for bone healing, pain reduction, and inflammation control has grown significantly in recent years. That’s why our clinic uses advanced Class 4 laser systems—to provide stronger, safer, and faster recovery outcomes for our patients.
How Does Laser Healing Therapy Work?
At its core, laser healing therapy is all about energy—specifically, the energy that your body needs to heal efficiently and effectively. It’s a high-tech way to stimulate biological change in your cells without the need for medications, needles, or invasive procedures.
When low-level or high-powered light from the therapeutic laser is applied to the skin, the light penetrates through the outer layers and reaches deeper tissues, including muscles, joints, and bone. Once there, this light energy is absorbed by the mitochondria within your cells. As mentioned earlier, mitochondria are the energy factories of your cells—and laser energy gives them a temporary boost, kind of like plugging your body into a biological charger.
This extra energy supports several healing processes, including:
- Increased ATP Production: So your cells have more energy to rebuild tissue.
- Improved Blood Flow: This brings oxygen and nutrients to the injured area.
- Reduced Inflammation: By decreasing pro-inflammatory compounds and encouraging tissue repair instead.
- Pain Relief: Through cellular repair and the stimulation of natural pain-relieving chemicals.
Laser therapy is cumulative in nature, meaning it builds on itself with each session. While you may feel some relief after the first treatment (some do), the real results tend to show up after a few consistent sessions—especially with deeper or more chronic injuries like fractures.
Whether you’re dealing with a fresh injury or something that’s been limiting you for months, laser healing therapy works by giving your body the energy and resources it needs to recover faster and more effectively.
Here are a few reasons you may want to look into Class 4 laser therapy for your musculoskeletal needs:
Key Benefits of Laser Healing for Bone Recovery
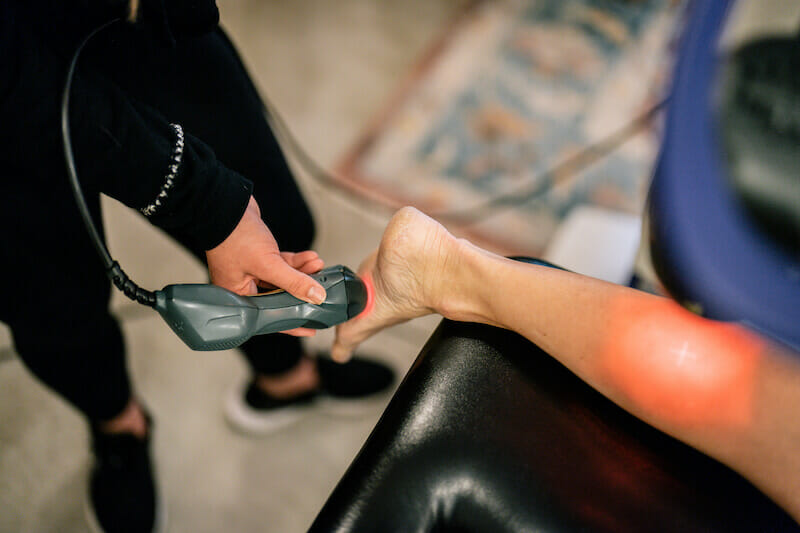

1. Laser Therapy Enhances Callus Formation
LLLT is known to have numerous effects on bone structure.
One particular effect that caught the attention of multiple experts is its ability to enhance callus development. But what is callus development? (1)
To answer that question, it’s best to discuss the steps of how bone heals in the body.
The bone healing process starts immediately after injury, but the actual callus formation begins about one week after you sustain an injury. The body begins by forming a soft type of bone called callus, which fills in the inflamed/injured area of the body.
The callus helps hold the bone together while the healing process continues, although the callus itself is not sturdy enough to resist pressure or tension. This is why injured individuals use casts or limit weight-bearing immediately after an injury — to support the injured area while the body transforms the callus into a new bone.
Over the next few weeks, the callus starts developing into a stronger bone that can withstand tension. After somewhere between two and eight weeks (depending on the severity and type of fracture), the callus should be strong enough to support gradual weight or pressure. Once this occurs, the patient can now remove the cast and use the previously injured body part at this point.
Under an X-ray, the part of the body where the bone is healing may look uneven. However, over the next few months, your body will automatically start reshaping the injured bone to go back to looking normal. (2)
A 2010 study shows that low-intensity laser therapy can accelerate the bone formation of the callus, from being soft to hard enough to withstand pressure.
This suggests you can accelerate bone healing with laser therapy. In other words, the fracture healing process, which usually takes anywhere from six to twelve weeks, can be sped up to reduce the overall recovery time of the injury.
Scientists also correlate that this particular effect of laser therapy can come in handy for non-union fractures. With non-union fractures, the healing process is abnormally slow, sometimes taking years to heal completely. (1)
2. Laser Therapy May Improve Healing in Facial Fractures
Facial fractures are one of the most common injuries a person can sustain in their lifetime. It may come from sports injuries, accidents, and even assaults. While the face may not require a cast, unlike wounds on the arms or legs, it can drastically reduce the quality of life of an individual. Fortunately, laser therapy has also shown promise regarding its facial bone healing effects.
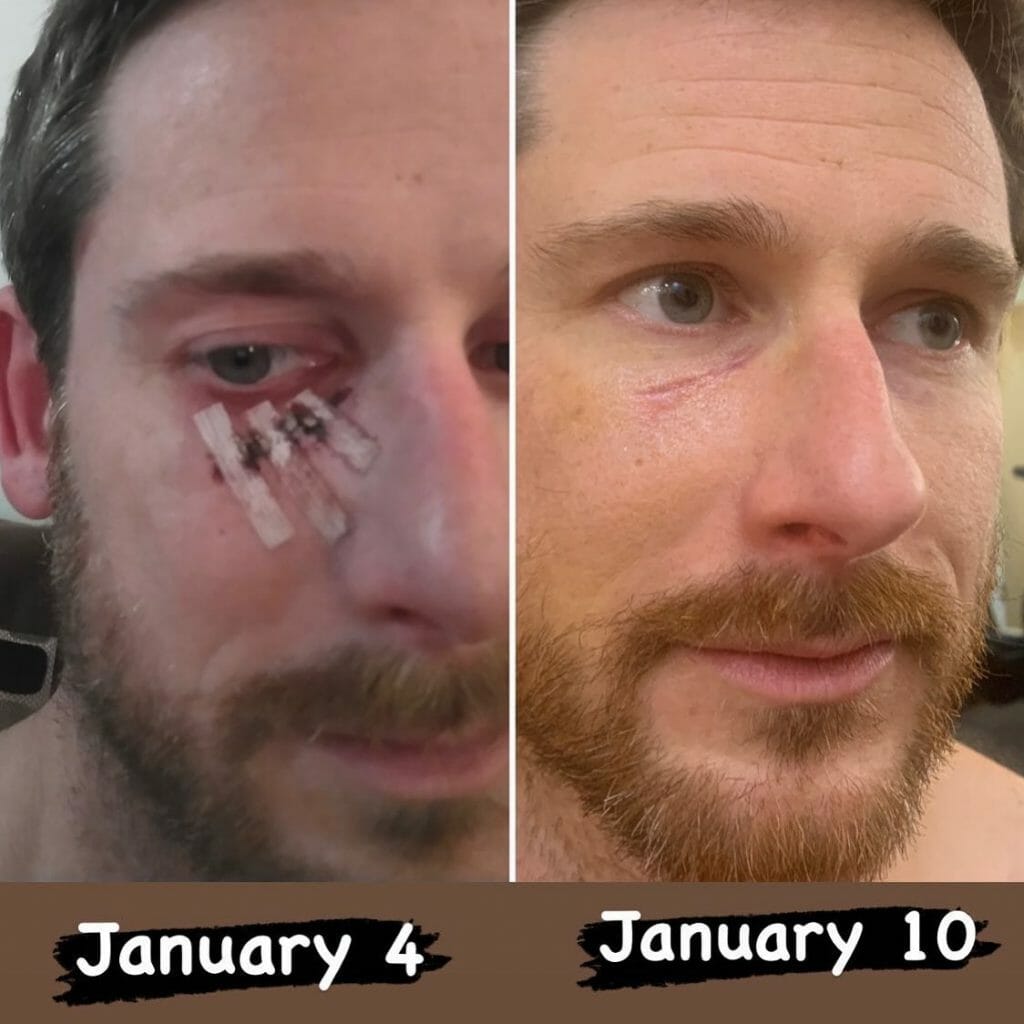
In a study consisting of 15 selected subjects, nine improved their facial bone defects after applying laser therapy, specifically, Low-Level Laser Therapy. To be more precise, there was an increase in bone mineral density, showing that the facial fractures healed faster than usual with laser therapy.
Furthermore, the study showed two other benefits that researchers think would be handy for injuries. (3)
3. Provides Drug-Free Analgesic and Anti-Inflammatory Relief
An analgesic is any intervention that relieves pain in the body. An anti-inflammatory is an intervention that reduces inflammation, redness, and swelling. There are corresponding medications for both, however, some of these medications can actually impede bone healing, so your doctor (or you) may prefer you avoid these medications while recovering from a bony injury like a fracture or surgery. Examples of these medications include:
- Aspirin
- Celecoxib
- COX-2 inhibitors
- Ibuprofen
- Naproxen (4)
The good news is that a class 4 laser has both analgesic and anti-inflammatory benefits, without the side effects some medications might have. This not only reduces the need for medications to control pain and swelling but also facilitates bony healing and regrowth.
Examples of bony injuries that can benefit from laser include:
Stress fractures, traumatic fractures, avulsion fractures, chip fractures, and surgeries such as ACL, UCL, or Rotator Cuff surgeries involving graft or tendon fixation into bone.
4. Stimulates Bone Regeneration Through Osteogenesis and Angiogenesis
According to a recent study conducted in 2021, laser therapy can potentially enhance the osteogenesis and angiogenesis processes in the body. These two processes make bone healing possible. (5)
Here’s a look at each process and what it has to do with bone healing:
- Osteogenesis is the process of creating new materials called osteoblasts that the body will use to form a new bone. It’s also often associated with osteoclasts—the cells that eat up the bone so it can reshape and realign it into more resilient and stronger structures.
- Angiogenesis is the creation of new blood vessels that serve as the route for cells like osteoblasts and osteoclasts, and bone tissues to reach the injury site. This process is crucial since adequate blood flow is necessary for bone regeneration. Moreover, complications may occur if there is an insufficient blood supply. (7)
By using laser therapy in Philadelphia, PA, to enhance the formation of bone tissues and blood vessels, patients can enjoy a faster, more comfortable recovery using their body’s own processes to do so.
Don’t Just Wait to Heal—Accelerate It
Waiting for a bone injury to heal on it’s own is perhaps one of the most frustrating situations to be in. Typical bone healing time (without the assistance of a device such as a Class 4 Laser) is among the longest of all musculoskeletal injuries, and many people find the pain and inflammation associated with fractures and other bone injuries to be severely life-limiting throughout the healing process.
Laser Therapy helps manage the pain and inflammation that makes the injury itself less limiting and facilitates the bony regeneration and tissue remodeling needed to support a faster recovery, as well as getting you back to whatever it is you love – sooner.
If you found this article helpful, or if someone you know has recently suffered an injury that would benefit from better bone healing through laser therapy, share this article with them, and let us know if you have any questions! Or, if you’re interested in learning more about our laser therapy in Philadelphia, PA, schedule a consultation by contacting us today.
References
- “Effect of low-level laser therapy on the fracture healing process”, Source: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19399356/
- “How Broken Bones Heal”, Source: https://kidshealth.org/en/parents/fractures-heal.html
- “Influence of low-level laser therapy on the healing of human bone maxillofacial defects: A systematic review”, Source: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S101113441630793X
- “Analgesics”, Source: https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/drugs/21483-analgesics
- “Low level laser therapy promotes bone regeneration by coupling angiogenesis and osteogenesis”, Source:https://stemcellres.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s13287-021-02493-5
- “Osteogenesis: The Development of Bones”, Source: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK10056/
- “Overview of Angiogenesis”, Source: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK53238/